-
https://www.inflearn.com/course/following-c-plus/dashboard
홍정모의 따라하며 배우는 C++ - 인프런 | 강의
만약 C++를 쉽게 배울 수 있다면 배우지 않을 이유가 있을까요? 성공한 프로그래머로써의 경력을 꿈꾸지만 지금은 당장 하루하루 마음이 초조할 뿐인 입문자 분들을 돕기 위해 친절하고 자세하
www.inflearn.com
객체지향의 기초
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std; // Object // Friend : name, address, age, height, weight, ... class Friend { public: // access specifier (public, private, protected) string _name; string _address; int _age; double _height; double _weight; void print() { cout << _name << " " << _address << " " << _age << " " << _height << " " << _weight << endl; } }; int main() { Friend jj{ "Jack Jack", "Uptown", 2, 30, 10 }; // instanciation, instance cout << &jj << endl; jj.print(); vector<Friend> my_friends; my_friends.resize(2); for (auto& ele : my_friends) ele.print(); return 0; }캡슐화, 접근지정자
클래스의 멤버 프로퍼티는 인스턴스로 직접 접근하여 수정하는 것보다는 access function을 따로 설정해서 접근하는 것이 유지보수 측면에서 좋다. (encapsulation)
private으로 설정하면 클래스 내부에서만 접근 가능하다.
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Date { private: // encapsulation int _month; int _day; int _year; public: // access function void setDate(const int& month_input, const int& day_input, const int& year_input) { _month = month_input; _day = day_input; _year = year_input; } void setMonth(const int& month_input) { _month = month_input; } const int& getDay() // getters { return _day; } // 같은 클래스의 다른 인스턴스의 멤버에도 접근 가능 void copyFrom(const Date& original) { _month = original._month; _day = original._day; _year = original._year; } }; int main() { Date today; today.setDate(8, 4, 25); today.setMonth(10); cout << today.getDay() << endl; Date copy; copy.copyFrom(today); cout << copy.getDay() << endl; return 0; }생성자 constructor
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Second { public: Second() { cout << "class Second constructor()" << endl; } }; class First { Second sec; public: First() { cout << "class First constructor()" << endl; } }; class Fraction { private: int _numerator; int _denominator; public: // constructor(생성자): instance가 만들어짐과 동시에 호출 Fraction(const int& num_in = 1, const int& den_in = 1) { _numerator = num_in; _denominator = den_in; cout << "Fraction() constructor " << endl; } void print() { cout << _numerator << " / " << _denominator << endl; } }; int main() { // 인자값을 넣지않을 땐 괄호를 뺸다 // Fraction frac; // Fraction frac{4,5}; // 타입변환을 하지 않음, 좀 더 엄격 Fraction frac(4, 5); frac.print(); First fir; return 0; }생성자의 Member Initializer List
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class B { private: int _b; public: B(const int& _b_in) : _b(_b_in) {} void print() { cout << _b << endl; } }; class Something { private: int _i = 100; double _d; char _c; int _arr[5]; B _b; public: Something() // Member Initializer List :_i(1), _d(3.14), _c('a'), _arr{ 1,2,3,4,5 }, _b(_i + 1) { _i *= 2; _d *= 3; //_c = 'a'; } void print() { cout << _i << " " << _d << " " << _c << " "; _b.print(); for (auto& e : _arr) cout << e << " "; cout << endl; } }; int main() { Something som; som.print(); return 0; }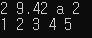
출력 결과 위임 생성자
// 위임 생성자 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class Student { private: int _id; string _name; public: Student(const string& name_in) : Student(0, name_in) // 위임 생성자 : 생성자가 생성자를 가져다 씀 {} Student(const int& id_in, const string& name_in) : _id(id_in), _name(name_in) {} void print() { cout << _id << " " << _name << endl; } }; int main() { Student st1(1, "heon"); st1.print(); Student st2("woo"); st2.print(); return 0; }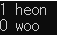
출력 결과 
'C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
C++) 연산자 오버로딩 (0) 2022.11.24 C++) destructor (1) 2022.11.23 C++) 함수 포인터 (0) 2022.11.22 C++) 인수 전달 방법 (0) 2022.11.22 C++) std::array, vector (0) 2022.11.22